Unlock the full potential of your two-way radio with these advanced features that cater to both casual users and professionals. Here’s a detailed guide to help you master subaudible tone scanning and frequency offset settings:
Subaudible Tone Scanning
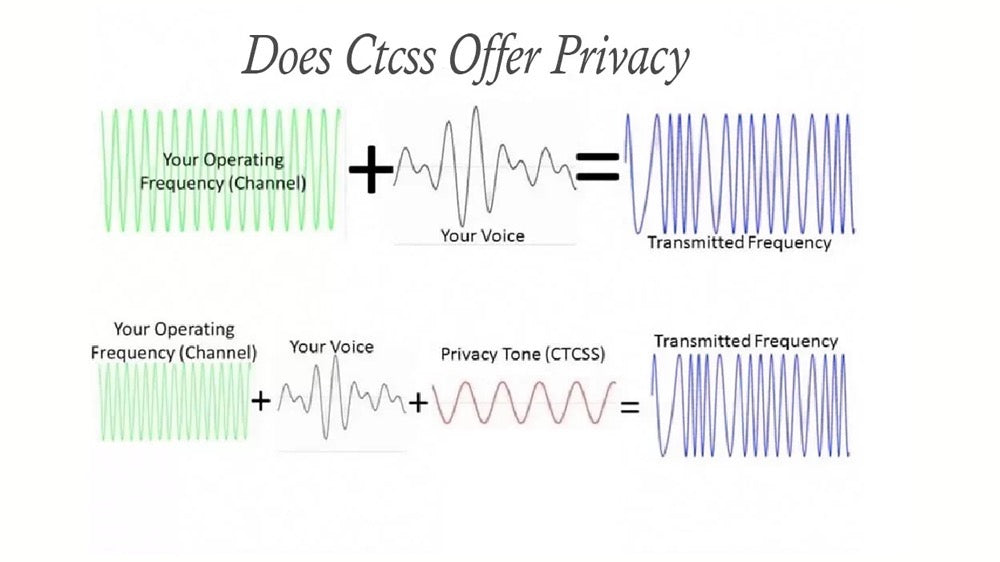
Subaudible tones are used in radio communication to allow access to certain channels or to activate specific features without interference from other transmissions. Understanding how to utilize these can significantly improve your communication effectiveness.
-
Scan Analog Subtones (Menu 06: SCAN CTCSS): This feature allows you to detect analog subtones used by other transmitters in your current frequency in Frequency Mode. The scan halts as soon as a subtone is detected, streamlining the process of connecting with compatible devices.
-
Scan Digital Subtones (Menu 07: SCAN DCS): Similar to analog, this function scans for digital subtones. It’s essential for identifying channels that employ digital squelch codes, which are more selective than analog tones.
-
Subtone Scan Storage (Menu 08: CDCSS SAVE MODE): Once subtones are detected, you can choose to save them:
- All: Saves both received and transmitted subtones.
- Receive Only: Saves only the received subtone.
- Transmit Only: Saves only the transmitted subtone.
Frequency Offset Settings
Frequency offset is crucial for accessing repeater systems, which require your transmit frequency to be different from your receive frequency.
-
Set Frequency Offset (Menu 09: SET): Adjust the offset to match the requirements of the repeater you are accessing, with a range from 00.000 to 99.995 MHz in Frequency Mode.
-
Frequency Offset Direction (Menu 10: S-D):
- Off: There is no offset between transmission and reception.
- Negative (-): Sets the transmit frequency as the sum of the receive frequency plus the offset, common for repeater access.
- Positive (+): Sets the transmit frequency as the receive frequency minus the offset, also used for repeaters.
Why It Matters
Mastering these settings not only enhances your ability to communicate effectively across various platforms but also ensures that your radio setup is optimized for clarity and reach in diverse communication environments.
📻 Enjoy Radio Time and elevate your two-way radio skills by implementing these advanced techniques to ensure seamless and clear communications, no matter where you are!











Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.